Written by Rami Taibah
Switching to Linux can be very daunting, most seasoned Linux users experienced that first hand. After all, at some point they were also “noobs”. However, the Linux community has excelled in making the switch for beginners as easy as possible by providing guides, howtos, tweaks, and general advocacy articles. When I first made the switch 3 years ago, I found the community welcoming me with open hands on forums, IRC channels, and E-mail, I was surprised how helpful these penguins were!
For this, I feel obliged to give back to the community that has always been there for me. To pass down the torch to newer Linux generations. Over here I compiled a list of 7 habits that I wish someone told me when I started out. I believe that getting into these habits will make the Linux experience more secure, convenient, educational, and ultimately more enjoyable.
1-Never Login Using ‘root’
If there was one habit that one should strictly abide by, it’s probably this one. Most of us come from a Windows background, and we have the notion that more power is better, so we login using our administrator accounts. Well let me tell you my friend, that this is a major reason that Windows is plagued with viruses and insecurities, half the world is currently running ‘root’ accounts!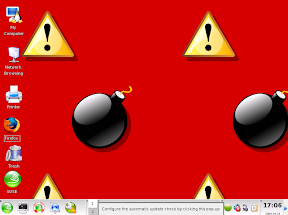 With great power comes great responsibility, and with ‘root’ powers you should be aware of the consequences of EVERYTHING you’re doing, and even then, mistakes happen. I remember my beginnings with SUSE Linux, there were lot of administrative tasks I needed to do but had no idea how to go about them without the GUI, so I so innocently log out and login onto the ‘root‘ GUI. The default wallpaper of the ‘root‘ GUI on SUSE were lit fuse bombs tiled beside each other. Back then, the symbolism totally flew over my head, coming from a Windows background, I wasn’t really doing anything wrong.
With great power comes great responsibility, and with ‘root’ powers you should be aware of the consequences of EVERYTHING you’re doing, and even then, mistakes happen. I remember my beginnings with SUSE Linux, there were lot of administrative tasks I needed to do but had no idea how to go about them without the GUI, so I so innocently log out and login onto the ‘root‘ GUI. The default wallpaper of the ‘root‘ GUI on SUSE were lit fuse bombs tiled beside each other. Back then, the symbolism totally flew over my head, coming from a Windows background, I wasn’t really doing anything wrong.
But what are the dangers of logging in as root?
- Well imagine you’re on the trapeze without a safety net, frightening isn’t it? Well that’s effectively what you are doing when you login as root, you can inadvertently hose your whole system
- You are at the risk of running malware. Any program that is started under root mode will automatically be given root privileges
- If there is a common security hole that hasn’t been patched yet, you could be totally “pwned”
- It’s common Unix convention, never run anything in root mode unless absolutely necessary. If a non-admin program asks for root access, you should be suspicious
Generally, instead of logging onto your root GUI, use any of the following techniques:
- Use “sudo” or “su” , and kill the session when your done
- If you don’t know how to do it in the command line, use “gksu” or “kdesu”. For example, press alt+f2 and type “gksu nautilus“. Close the app as soon as you finish
2-Properly Name Your Files
In a Linux environment, you can name your files whatever you want except for, 1) the forward slash “/” which is reserved for the root directory, and 2) a null character. Anything else is technically acceptable, however there are some best practices that you should abide by in order to avoid any future complications:
- As a rule of thumb, only use alphanumeric characters, hyphens, periods, and underscores
- Avoid special symbols like dollar signs, brackets, and percentages. These symbols have special meanings to the shell, and could cause conflicts
- Avoid using spaces, handling files with spaces in the terminal is kind of awkward. Replace spaces with either hyphens or underscores
I personally have grown into this habit, I find myself following these guidelines even in a Windows or Mac environment.
3-Place /home on a Different Partition
![]()
Doing this gives you extreme flexibility, a kind that you never imagined before. Having /home in a separate partition enables you to reinstall your system or even change your whole distro without losing your data and personal settings. Just keep the “/home” partition intact and reinstall whatever you want on your “/”. Now you can try out distros as much as you want, without worrying about your data and personal settings, they go with you on the go ;).
If you weren’t lucky enough to know this before installing your system, then do not despair! Carthik from Ubuntu Blog takes you in a step-by-step guide titled “Move /home to it’s own partition”
4-Proper Crash Management
 Linux is very robust and stable, however every system can come down to it’s knees every once in a while. Before you head to CTRL-ALT-DEL, the restart button, or the plug, you should know how to properly handle any crash. As opposed to another un-named operating system, you should be able to easily recover your system without actually restarting! I personally go through different levels, if one doesn’t work I elevate it to next step:
Linux is very robust and stable, however every system can come down to it’s knees every once in a while. Before you head to CTRL-ALT-DEL, the restart button, or the plug, you should know how to properly handle any crash. As opposed to another un-named operating system, you should be able to easily recover your system without actually restarting! I personally go through different levels, if one doesn’t work I elevate it to next step:
- I have the “force quit” applet on my taskbar, if any app starts to act up just click on the “force quit” icon and then kill the app
- If that doesn’t work, draw up a terminal and type “ps -A” , and take note of the Process ID (PID) of the culprit app, then kill it. “kill PID”
- Use the “killall” command, for example,
“killall firefox-bin” - If your whole GUI is frozen, and drawing up a terminal is impossible, then press CTRL-ALT-F1, this will take you to another terminal, and virtually a whole new session. From there kill the culprit app using step 2 and 3.
- If that doesn’t work, you might want to restart your GUI using the CTRL-ALT-Backspace combo. Beware, that this will kill all your GUI apps currently running
- Invoke CTRL-ALT-F1 and do CTRL+ALT+DEL from here. This will not instantly reset your system, merely perform a standard reboot, it’s safe. (Assuming you want to restart and CTLR-ALT-F1 works)
- Finally if nothing works, don’t rush to the hard reset button, try to Raise a Skinny Elephant
5-Play The Field

You were probably recruited to your current distro by a friend, it suited you, and stuck with it. That’s great, but there is probably something better for you out there. Why not harness the flexibility and richness of Linux and Open Source? Don’t be afraid to experiment around with different distros, apps, window managers, and desktops. Experiment until you find the best fit. Think of it this way, if you are currently living in the best place on earth for you, traveling around the world wouldn’t really harm right? In fact you might find a better place to live in, but if you didn’t, the time you spent traveling would not have gone to waste, you would have learned a lot about other countries, other people and traditions, different ways of thinking, and ultimately had fun!
Every new thing you try out will contribute to your incremental learning, in a year’s time you will have a good grasp on Linux and the Open Source world. I personally tried out at least 10 distros, 4 desktops, and 5 window managers. My recent article Etymology of A Distro got me interested in a couple more distros such as Zenwalk, Foresight, and Sabayon. Play the field, my friend, it will do you good.
But before you proceed, pay heed to these few hints:
- Set up your perfect system that you feel comfortable with, you need a workable system 24/7 right? Then test around using one of the below points
- Harness the power of virtualization! Install Vmware or Virtualbox. Use them to test out the distros
- Alternatively, if you are not big on virtualization, you can set up a separate partition to test new distros. A partition that you couldn’t care less about
- Ultimately, you can have a main PC and a test one. Wreak havoc on the test one
Anime image is licensed by Creative Commons BY-NC 3.0
Original Artwork by Juzo Kun, Modified by Wayne Richardson.
6-Nurture Your CLI Adoption
Now I am not going to advocate learning the command line, there are numerous articles that emphasise on it’s importance. What I am assuming here is that you already know it’s importance, and have a rudimentary understanding on how to do some simple administrative tasks. You are already hacking away, tweaking and configuring, following the different guides and howtos scattered all over the tubes, but don’t just copy and paste!! Meaning, instead of just headlessly executing commands some random guy half way across the world told you to execute, try to understand what every command does. Why did the guide ask you to do this, as opposed to something else? Understand the rationale of the steps you are asked to do. These commands are highly relevant to you, and will help you gain a better understanding than any 101 guide.
After a while you will notice that you have amassed a good deal of CLI lore.
At the end of the day it’s just a pseudo-language! Every command is probably just an acronym of something, or a cut down version of a real word. You expect your dog to understand “Spike fetch ball” so why don’t you expect to understand “sudo mv /file1 /file2??
7-Always Be Ready to Unleash The Power Within
 Personally, I had numerous occasions when a friend asked me to do something on his/her computer, but found myself crippled because of his/her choice of OS. At other times I wanted to do something urgently but the only computer had another crippled OS. Spare yourself the agony, have Linux with you all the time, whether it’s on a USB pendrive, a live CD, or even a live CD business card ! There are dozens of good Linuces out there that are perfect for on-the-go computing. Knoppix, DSL, and Puppy Linux are just a few examples.
Personally, I had numerous occasions when a friend asked me to do something on his/her computer, but found myself crippled because of his/her choice of OS. At other times I wanted to do something urgently but the only computer had another crippled OS. Spare yourself the agony, have Linux with you all the time, whether it’s on a USB pendrive, a live CD, or even a live CD business card ! There are dozens of good Linuces out there that are perfect for on-the-go computing. Knoppix, DSL, and Puppy Linux are just a few examples.
I personally don’t apply this habit, which is a shame, I really need to get my act together! :p </publishes and heads to pendrivelinux.com>
why do you use “your done” instead of “you’re done” and “it’s importance” instead of “its importance”?
Nice article. Although I’d change the title of #5 to something more meaningful like “Expirement with different distributions”. All of your titles are (somewhat) self explanatory except for #5.
Good job though. I very much agree with your list.
Possibly another one to add is putting the SWAP partition at the beginning of the drive. Or when installation is complete, it’s still not complete because the system needs to be honed and tweaked for performance gains.